Dr. Aubrey N. Beal takes us through the process of designing a temperature regulation device for a DNA replication process using a Peltier device, H-bridge and Arduino controller. Dr. Beal is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering at the University of Alabama in Huntsville. Dr. Beal teaches undergraduate and graduate courses in signal processing and electronics. His research interests include nonlinear dynamics and chaos.
- What did you think about Dr Beal’s presentation?
- Would you like to learn more about electrical engineering? Have you taken classes or taught yourself any computer programming?
- Can you think of other ways that Peltier coolers might be used?
Earn badges and qualify for prize drawing by registering and answering journal questions. It's fun and easy!
Peltier Device
As describe on Wikipedia, a Peltier device or “thermoelectric cooler module” uses the Peltier effect to create a heat flux at the junction of two different types of materials. A Peltier cooler, heater, or thermoelectric heat pump is a solid-state active heat pump which transfers heat from one side of the device to the other, with consumption of electrical energy, depending on the direction of the current. It can be used either for heating or for cooling, although in practice the main application is cooling. It can also be used as a temperature controller that either heats or cools.
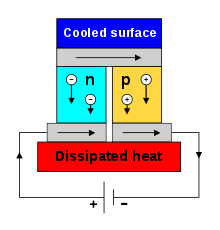 When an electric current is passed through a circuit of a thermocouple, heat is evolved at one junction and absorbed at the other junction. This is known as the Peltier Effect. The Peltier effect is the presence of heating or cooling at an electrified junction of two different conductors and is named after French physicist Jean Charles Athanase Peltier, who discovered it in 1834.
When an electric current is passed through a circuit of a thermocouple, heat is evolved at one junction and absorbed at the other junction. This is known as the Peltier Effect. The Peltier effect is the presence of heating or cooling at an electrified junction of two different conductors and is named after French physicist Jean Charles Athanase Peltier, who discovered it in 1834.
Learn more about thermoelectric cooling: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermoelectric_cooling
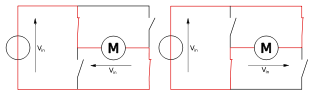
H-Bridge
 According to Wikipedia, an H-bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backwards. H bridges are available as integrated circuits, or can be built from discrete components. Here’s a circuit diagram:
According to Wikipedia, an H-bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backwards. H bridges are available as integrated circuits, or can be built from discrete components. Here’s a circuit diagram:
As shown the direction of current can be changed by opening an closing the corresponding switches.
Learn more about the H-bridge: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H-bridge
Arduino
 Arduino micro-processors are low-cost open-source micro controllers popular in the hobbyist community. For under $20 an Arduino kit can be purchased and used in a variety of electronics projects. According to Wikipedia …
Arduino micro-processors are low-cost open-source micro controllers popular in the hobbyist community. For under $20 an Arduino kit can be purchased and used in a variety of electronics projects. According to Wikipedia …
Arduino board designs use a variety of microprocessors and controllers. The boards are equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards (‘shields’) or breadboards (for prototyping) and other circuits. The boards feature serial communications interfaces, including Universal Serial Bus (USB) on some models, which are also used for loading programs. The microcontrollers can be programmed using the C and C++ programming languages, using a standard API which is also known as the “Arduino language”. In addition to using traditional compiler toolchains, the Arduino project provides an integrated development environment (IDE) and a command line tool (arduino-cli) developed in Go.
The Arduino project began in 2005 as a tool for students at the Interaction Design Institute Ivrea in Ivrea, Italy,[2] aiming to provide a low-cost and easy way for novices and professionals to create devices that interact with their environment using sensors and actuators. Common examples of such devices intended for beginner hobbyists include simple robots, thermostats and motion detectors.
The name Arduino comes from a bar in Ivrea, Italy, where some of the founders of the project used to meet. The bar was named after Arduin of Ivrea, who was the margrave of the March of Ivrea and King of Italy from 1002 to 1014.
Learn more about Arduino: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arduino